使用期限租赁或永久
许可形式单机和网络版
原产地美国
介质下载
适用平台window,mac,linux
科学软件网专注提供科研软件。截止目前,共代理千余款,软件涵盖各个学科。除了软件,科学软件网还提供课程,包含34款软件,66门课程。热门软件有:spss,stata,gams,sas,minitab,matlab,mathematica,lingo,hydrus,gms,pscad,mplus,tableau,eviews,nvivo,gtap,sequncher,simca等等。
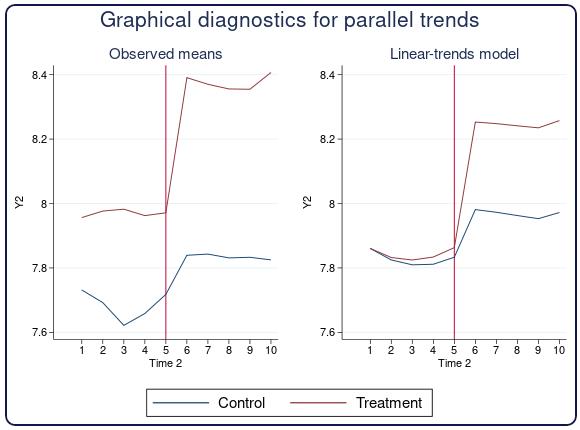
Panel-data ERMs
Extended regression models (ERMs) were a big new feature last release. The ERM commands fit models that account for three common problems that arise in observational data—endogenous covariates, sample selection, and treatment—either alone or in combination.
In Stata 16, we introduce the xteregress, xteintreg, xteprobit, and xteoprobit commands for fitting panel-data ERMs. This means ERMs can now account for the three problems we mentioned above and for within-panel correlation. These new commands fit random-effects linear, interval, probit, and ordered probit regression models. They allow random effects in one or all equations, and they allow random effects to be correlated across equations.
Researchers from all disciplines who work with observational (nonexperimental) data are interested in ERMs and will be excited about the new panel-data versions of these commands. However, different disciplines talk about these models differently.
Above, we referred to the problems ERMs solve as endogenous covariates, sample selection, treatment, and within-panel correlation. While this terminology is common in some disciplines such as economics, other disciplines may use other terms.
• Instead of panel-data and within-panel correlation, researchers may ask for models for multilevel (two-level) data that account for within-group correlation.
• Instead of endogenous covariates, researchers may ask for methods of dealing with unobserved confounding or unmeasured confounding.
• Instead of sample selection, researchers may be concerned about trials with informative dropout, nonignorable nonresponse, or outcomes missing not at random (MNAR).
• Instead of treatment, researchers may ask about methods for causal inference or estimating average treatment effects (ATEs).
The important message is that all disciplines are interested in ERMs, but they often speak different languages.
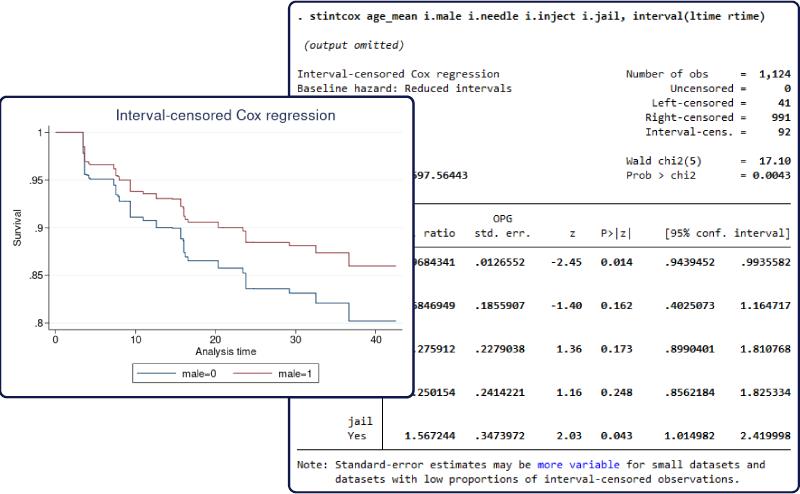
ziologit is the answer.
Most applications of rank() will be to one variable, but the argument exp can be more general,
namely, an expression. In particular, rank(-varname) reverses ranks from those obtained by
rank(varname).
The default ranking and those obtained by using one of the track, field, and unique options
differ principally in their treatment of ties. The default is to assign the same rank to tied values
such that the sum of the ranks is preserved. The track option assigns the same rank but resembles
the convention in track events; thus, if one person had the lowest time and three persons tied for
second-lowest time, their ranks would be 1, 2, 2, and 2, and the next person(s) would have rank 5.
The field option acts similarly except that the highest is assigned rank 1, as in field events in which
the greatest distance or height wins. The unique option breaks ties arbitrarily: its most obvious use
is assigning ranks for a graph of ordered values. See also group() for another kind of “ranking”.
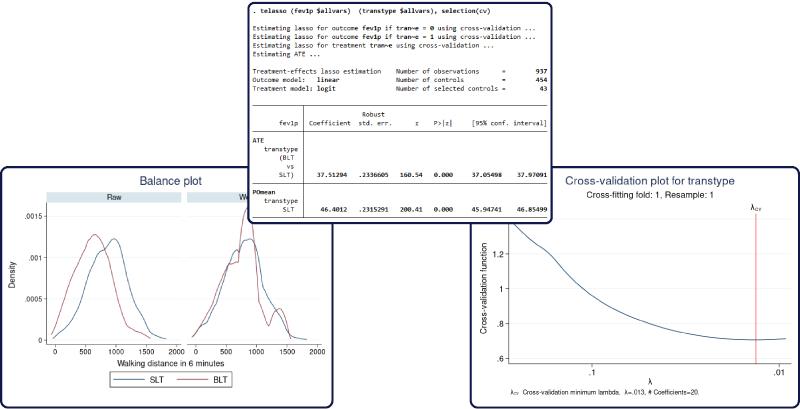
Causal inference, average treatment effects, potential-outcome means, double-robust estimation
,专注,专心是科学软件网的服务宗旨,开发的软件、传递*的技术、提供贴心的服务是我们用实际行动践行的目标,我们会为此目标而不懈努力。
http://www.kxrjsoft.com.cn








